721 Exchange/UPREIT Structure 721 Exchange/UPREIT Structure
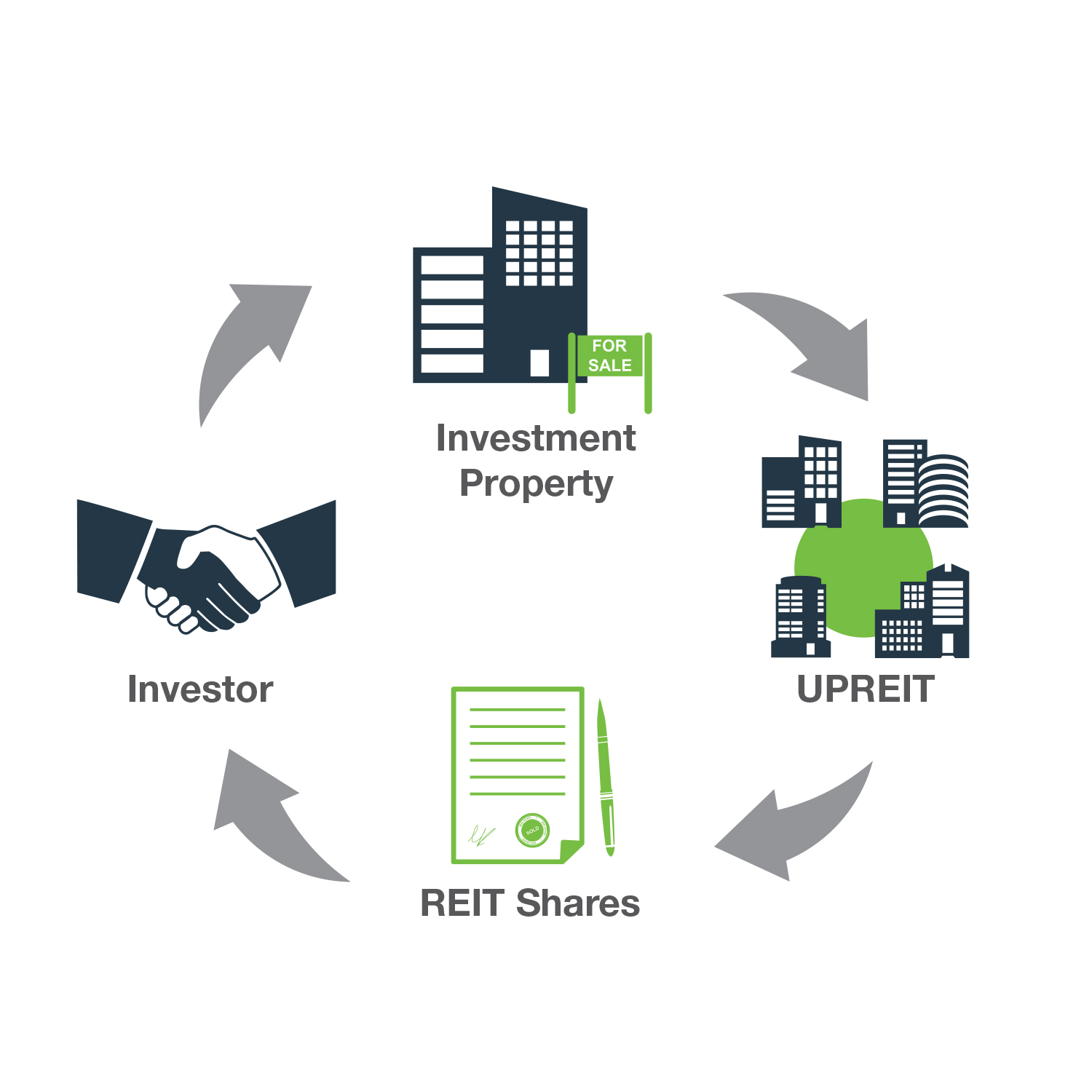
A 721 exchange allows real estate property owners to contribute property, on a tax-free basis, in exchange for interests in an operating partnership of a real estate investment trust (REIT). To complete a successful 721 exchange transaction, the REIT must be structured as an umbrella partnership real estate investment trust, or UPREIT.
A 721 exchange allows real estate property owners to contribute property, on a tax-free basis, in exchange for interests in an operating partnership of a real estate investment trust (REIT). To complete a successful 721 exchange transaction, the REIT must be structured as an umbrella partnership real estate investment trust, or UPREIT.
In an UPREIT transaction, a property owner looking to defer taxable gain on the sale of a property may transfer the property to the UPREIT in exchange for limited operating partnership units (OP Units). Taxes on the gain are deferred until the seller later redeems the OP Units for shares of the REIT. Although a powerful tax deferral and diversification strategy for real estate owners to consider, 721 exchanges are complex and may not be suitable for all investors.
Potential Benefits of a 721 Exchange/UPREIT Structure
Frequently Asked Questions
Can 1031 exchange be performed after a 721 exchange?
REIT shares are not eligible to be used in a 1031 exchange, therefore once a 721 exchange is completed, capital gains taxes can no longer be deferred via a 1031 exchange.
Can DST interests be used in a 721 exchange?
Property owners can contribute DST interests to an UPREIT in exchange for OP Units as part of a 721 transaction. Taxes on this transaction are deferred during the time the OP Units are held, typically between 12 to 24 months. Investors may receive distributions from OP Units*.
How does a 1031 exchange differ from a 721 exchange?
Both transactions allow property owners the ability to defer capital gains tax on the sale of a business or investment real property. However, a 721 exchange transaction allows property owners to contribute real property in exchange for interests in an operating partnership of a REIT that is structured as an UPREIT. With a 1031 exchange, property owners exchange property for other like-kind property.
For More Information
Inland Private Capital investment programs are sold by broker dealers and registered investment advisors authorized to do so.
Contact your financial professional to learn more. Or, for help finding a financial professional:
Inland Private Capital Investment Programs are sold by broker dealers and registered investment advisors authorized to do so.
Connect with your Inland team to learn more: